本文记录了如何将 Vue 语言转译为 React 语言。主要目的是,当你面对此类源代码分析工作时,能够找到一些结构化处理的思路。
背景
标题中的 Vue 加上了引号,因为要转译的 Vue 代码不是包含了所有 Vue 语言特性的代码,而是 Vue 的一个子集。Cube 技术解读 | 支付宝新一代动态化技术架构与选型综述 这篇文章介绍了支付宝中使用的动态化框架,“对于Cube卡片,支持基于精简vue的card-dsl。”
Cube 卡片是一种客户端技术,进行 Cube 卡片研发需要进行繁琐的开发环境配置,将 Vue 转译为 React 能够在浏览器中实时预览,提升研发效率。将精简的 Vue 语法转译为标准的 Vue 语法也能实现浏览器预览,但公司里的 H5 项目均采用 React 开发,转译为 React 能够在 H5 项目中复用已有的 Cube 卡片。
暂将这个工具命名为 CubeTrans。
工具
工具库
vue-template-compiler
从 *.vue 文件中解析出 template / script / style。
@babel/parser
将源代码解析成 AST (Abstract Syntax Tree,抽象语法树)。
@babel/traverse
遍历 AST。@babel/traverse 会以深度优先搜索的方式遍历 AST。
@babel/types
AST 中节点类型的定义,也可以创建新的 AST 节点。比如:
判断节点类型:
t.isMemberExpression()/t.isIdentifier()创建节点:
t.memberExpression(t.thisExpression(), t.identifier('state'));
@babel/generator
从 AST 生成源代码。
辅助工具
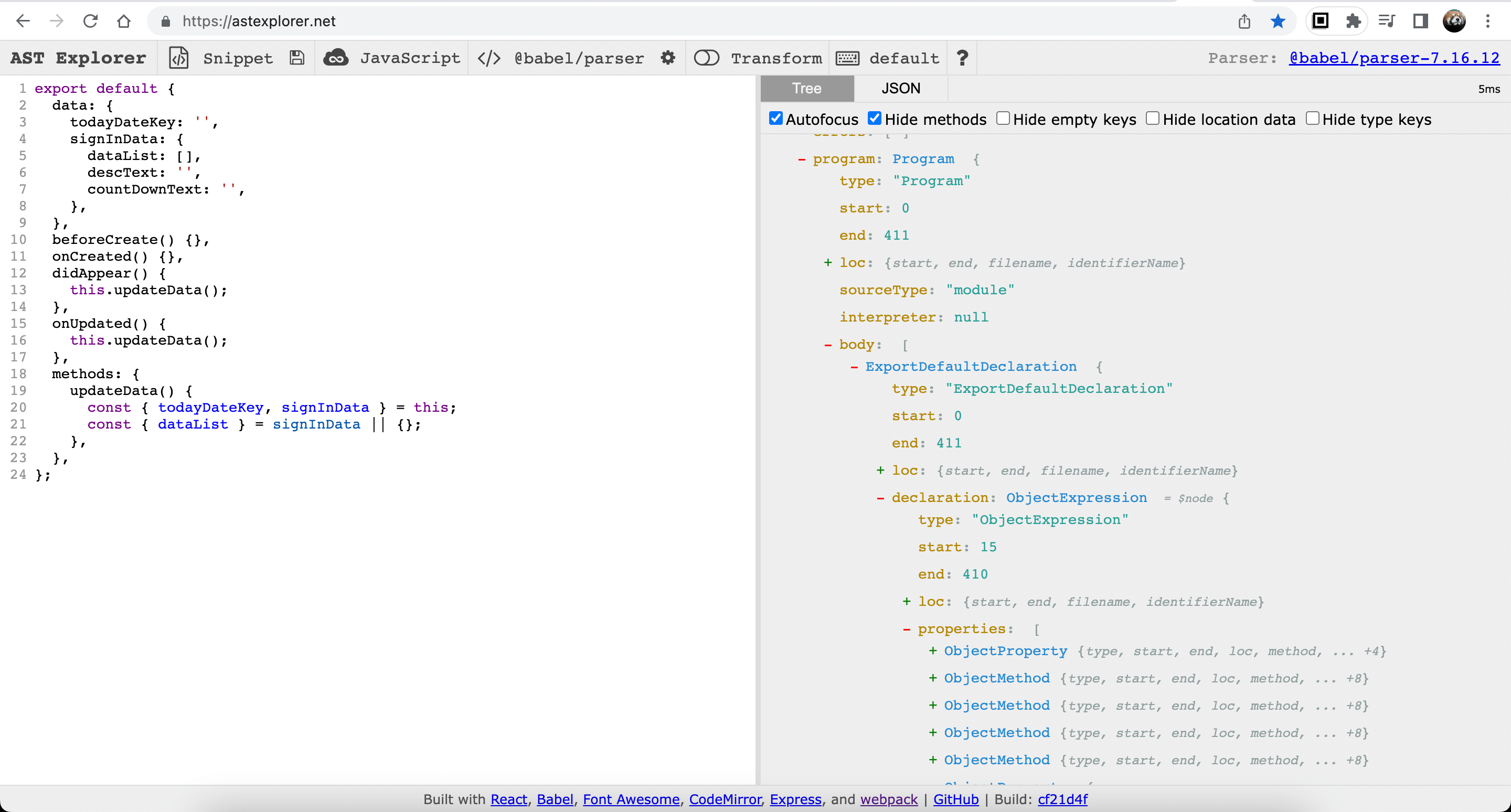
AST Explorer
查看源代码对应的 AST。AST 相关开发必备工具。
问题分析
效果预览
下面是转译前后的代码。
Vue 代码:
1 | <template> |
React 代码:
1 | import React from 'react'; |
1 | .example { |
问题拆解
- React 与 Vue 的差异点在哪里?需要做什么样的转换?
如上面效果预览所示,转译前的 Vue 代码为单文件组件,转译后为 React 类组件。
从代码结构来说,Vue 的 template 部分转译为 React 的 render 方法,Vue 的 script 部分转译为 React 的类方法,Vue 的 style 部分转译为 CSS。CubeTrans 的处理模块与此一一对应,即针对 template / script / style 分而治之、处理 script 时以类方法作为突破口。
从代码语句来说,主要任务是修改访问类属性的方式。Vue 中类属性挂在 this 下面,React 中类属性挂在 this.state 下面。
- 如何遍历代码?
我们需要一种方式来遍历 Vue 的每一行代码,当遍历到目标代码时,将其转移为 React 的实现。
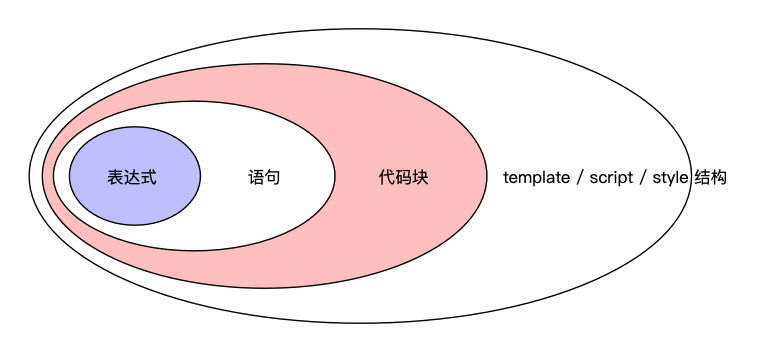
上图描述了 CubeTrans 视角的 Vue 代码的组成结构。最小结构是表达式,其次是语句,再然后是代码块,最后是 template / script / style 结构。
template / script / style 结构很简单,直接硬编码就能遍历到。语句也很简单,每一行代码对应一条语句,可以直接顺序遍历。
代码块是包含在一对花括号之间的代码,比如函数体、条件分支、循环体、try catch 块、switch case 块等。CubeTrans 使用广度优先搜索算法来遍历代码块。
表达式虽然是最小组成结构,但它的复杂程度也各不相同。比如,三元运算表达式可能包含了函数调用表达式和逻辑计算表达式。遍历表达式使用深度优先算法来实现,即不断的进行函数递归调用,直至找到最简单的表达式,然后进行转译。
转译
数据结构
自定义数据结构
- Collect
保存所有已完成转译的 AST 节点。基于此数据结构数据,可以生成 React 代码。
1 | interface Collect { |
- State
保存全局上下文信息。
1 | interface State { |
- MethodTraverseContext
上文说到 CubeTrans 处理 script 时以类方法作为突破口,MethodTraverseContext 即用于保存类方法处理过程的上下文信息。
1 | interface MethodTraverseContext { |
工具库的数据结构
- node
AST 中的节点称为 node。
@babel/types 判断节点类型,传入的参数即为 node。@babel/types 创建节点,生成的实例也是 node。
- path
@babel/traverse 遍历 AST 会生成 path 对象。@babel/traverse 提供的遍历函数,会以深度优先搜索的方式遍历 AST。
使用 path 可以在 AST 中移动,如: path.parentPath -> 获取父节点,path.get('xxoo.xxoo') -> 获取子节点,path.skip() -> 跳过子节点。
path.node 返回对应的 AST node 节点。
- 修改 node 或 path,都能够修改 AST
如: path.replaceWith(),node.callee = t.memberExpression(node, node)
整体流程
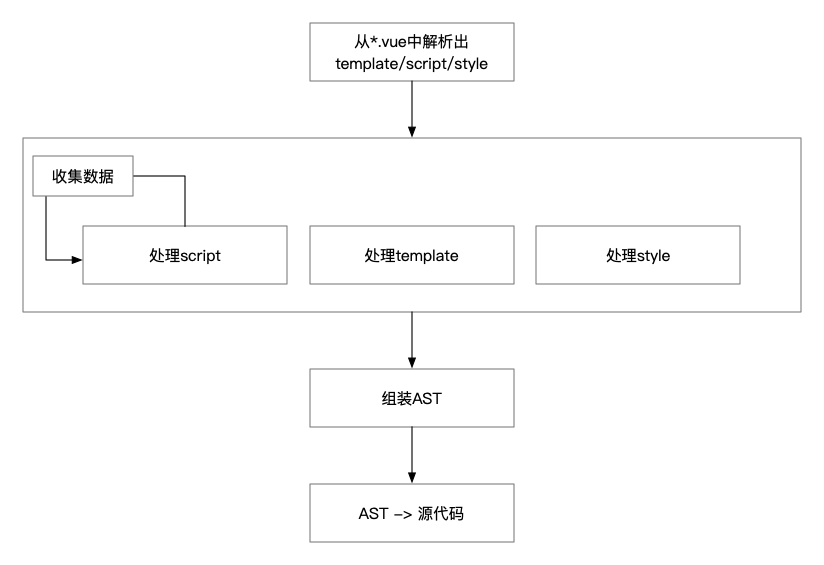
- 使用
vue-template-compiler从原始代码中解析出 template / script / style 三部分。
1 | const sourceCode = fs.readFileSync(srcPath, 'utf8'); |
分别处理 template / script / style 转译为 React 代码。其中 script 部分的处理逻辑最复杂,需要多次循环处理,收集数据;template 的处理难度次之;最后是 style。
处理过程中生成的数据保存在 Collect 数据结构中。遍历并处理完所有代码后,CubeTrans 从 Collect 中取出数据并组装成 AST。
使用
@babel/generator从 AST 生成 React 源代码。
处理 script
一句话说明
遍历所有代码,并在访问到特定代码时进行转译,如:
this.xxoo写法转译成this.state.xxoo;this.xxoo = 'aabb'写法转译成this.setState({ xxoo: 'aabb' });
整体流程
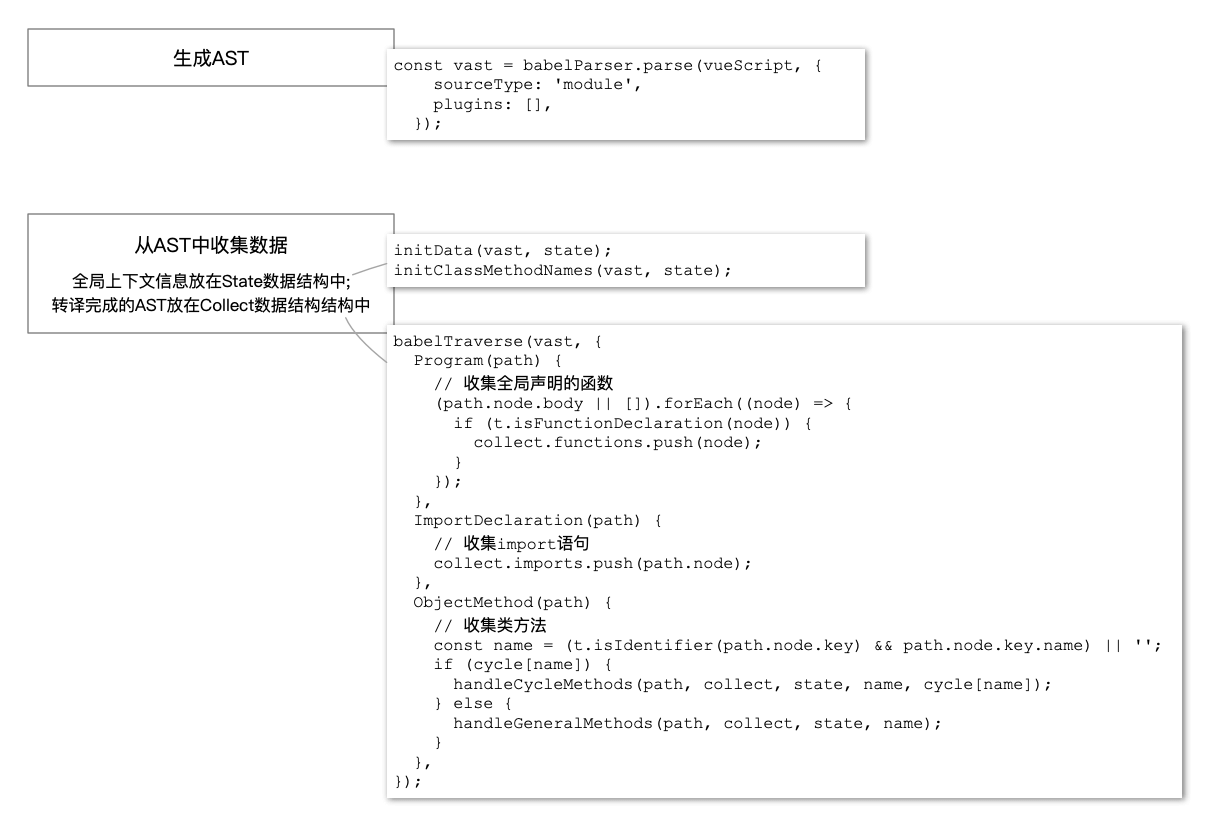
类方法处理流程
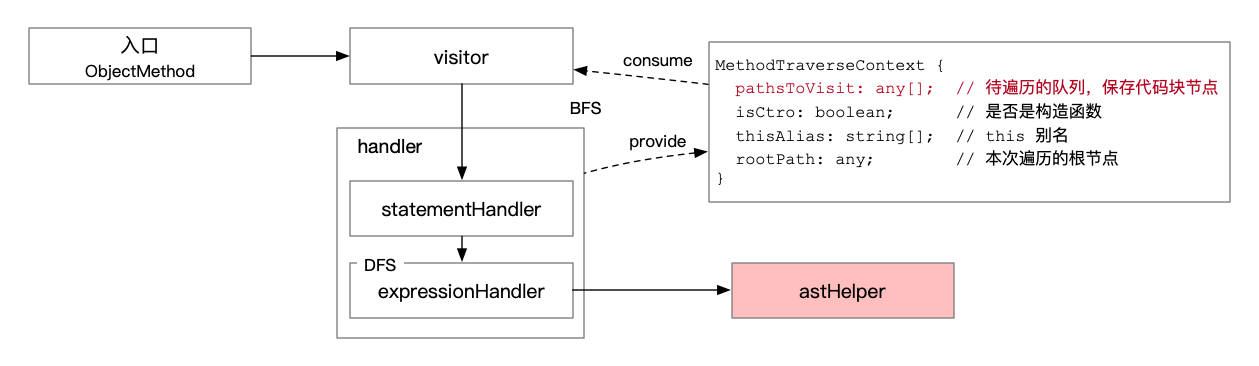
CubeTrans 的最小处理单元是类方法。
使用广度优先搜索(Breadth-First Search,BFS)算法遍历
代码块。使用深度优先算法(Depth-First-Search,DFS)遍历
表达式。- 一次处理流程从类方法进入。
pathsToVisit是进行广度优先搜索的核心数据结构,保存了待访问的代码块节点。- visitor 负责从
pathsToVisit中取出待处理节点,执行遍历。 - handler 需要理解并处理 AST:转译代码,或者将代码块放入
pathsToVisit中。 - handler 包含了语句处理器和表达式处理器。遍历表达式时,若遇到复杂表达式则递归处理(深度优先遍历),直至遍历到最简单的表达式后执行转译。
- astHelper 中提供了常用的转译处理函数。即执行上面一句话说明里的任务。
- 递归处理表达式
1 | /** |
处理 template
一句话说明
遍历所有代码,并在访问到特定代码时进行转译。需要转译的代码有两类:一类是 Vue 模板;一类是 JS,包括 Vue 指令和 JSXExpression。
整体流程
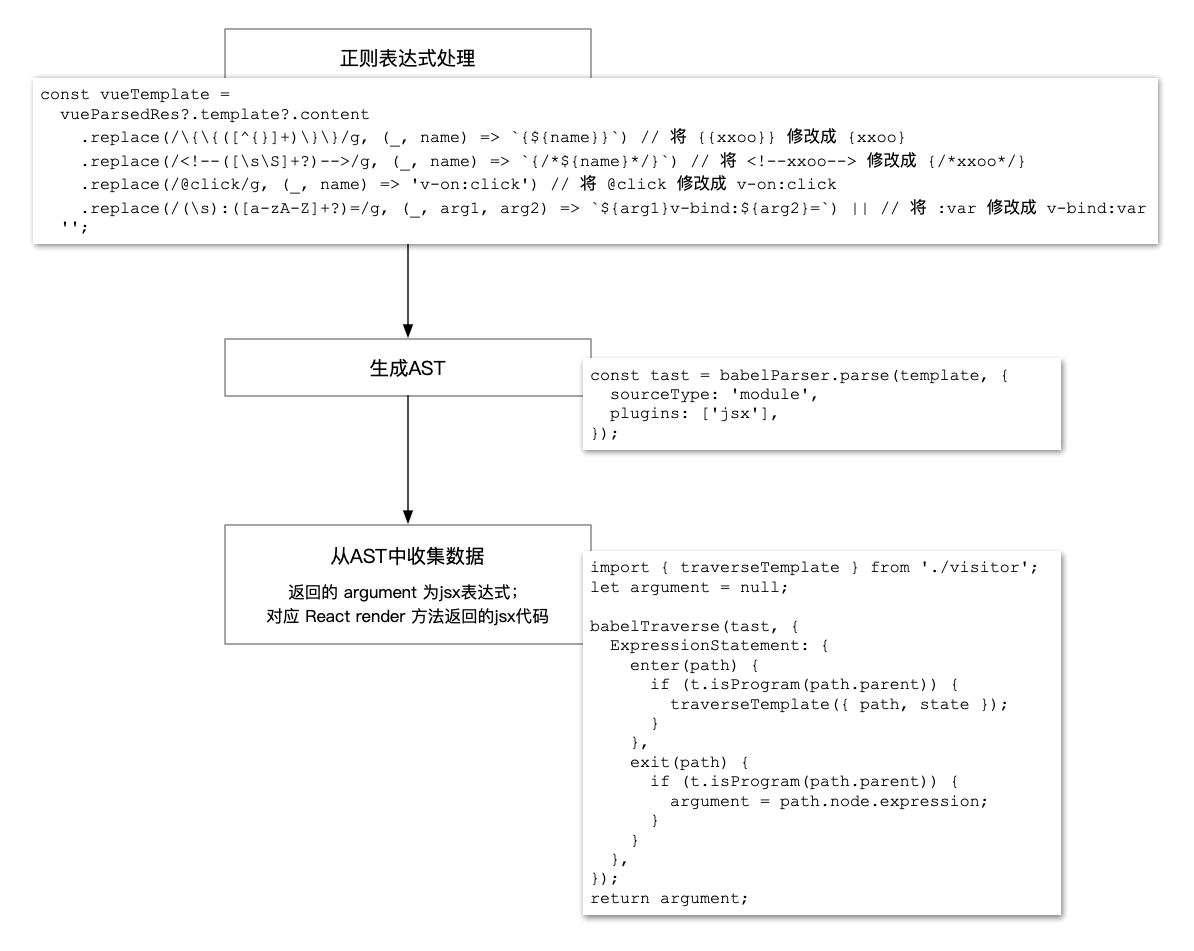
template 需要使用正则表达式进行预处理,随后才能被 @babel/parser 解析为 AST。
处理流程
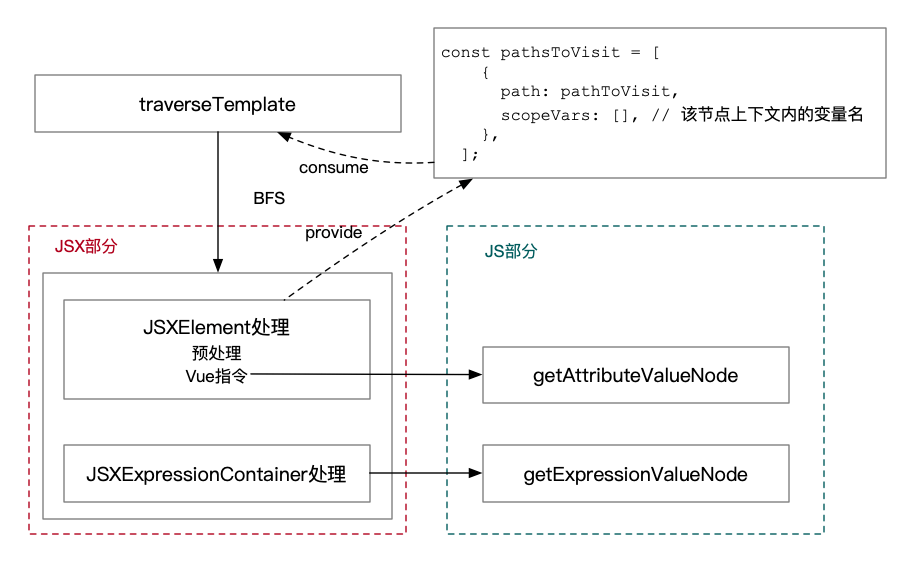
使用广度优先搜索算法遍历 AST。
template 的处理分为 JSX 与 JS 两部分。
JSX 部分的工作是将 Vue 模板转译为 React JSX 语法。比如下面这些 Vue 指令都需要进行处理:
- v-if / v-if-else / v-else
- v-for
- v-show
- v-on
- v-bind
JSXElement 预处理的工作是删除或转换 Cube 卡片自定义的标签,如 image 标签转为 img 标签。
涉及到 JS 语言的部分,如 Vue 指令和 JSXExpression,会交给 JS 部分处理。具体逻辑如下:
1 | function wrapIdentifier(path, scopeVars) { |
处理 style
CSS 通常遵循 web 规范,无需额外处理。如果需要处理,有些工具库可以利用,如 csstress。
Bad Case
React setState 在一些情况下异步执行,下面的代码转译后,运行时效果可能不符合预期。
1 | this.a = 1; |
1 | this.setState({ a: 1 }); |
最佳实践
vscode debug
断点调试功能对此类纯逻辑功能项目的开发非常有用。
创建一份配置,即可以使用 vscode 的调试功能。
1 | { |
测试驱动的开发
测试库:
jest方案:snapshot 比对。
- 输入为各种 case 的 Cube 卡片代码;输出为转译后的 React 代码,保存为 snapshot;
- 测试通过的条件是,本次转译后的 React 代码与 snapshot 一致;
总结
最初的灵感来源是 vue-to-react 这个库。vue-to-react 尝试将标准的 Vue 代码转译为 React,但是看代码并没有一套结构化的处理流程,转换失败的 case 很多。目前是无人维护的状态。
AST 处理的工具库很多,看 https://astexplorer.net/ 下拉列表的长度就能发现。本文以 Vue 代码转译为 React 代码作为实际案例,进行剖析。希望你在进行其它 AST 分析的任务时,本文中的知识点能有所启发。
